
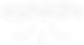
43%
emissions reduction needed by 2030 to meet our 1.5-degree goal. Current countries’ plans lead to 11% increase.
[UN IGPCC]
.png)
2%
of global wealth is owned by the bottom 50% of the global population. The top 10% own 76%. The socio-economic divide is growing.
[World Inequality Report 2020]
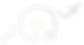
> 10%
of income spent on energy for 13% of US households. In Europe, 16% of households face a high energy burden and 8% cannot afford to keep warm.
[European Parliament, American Council for Energy Efficient Economy, 2020]

70%
of global greenhouse gas emissions come from upper-middle- and high-Income countries.
[Our World in Data]
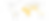
> 50%
of global emissions likely to arise from developing countries (excluding China) by 2030, making it impossible to reach global “net zero” by midcentury.
[Brookings, Foreign Affairs]
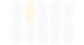
1 in 10
people globally have no access to electricity and live in extreme poverty.
[World Bank, IEA]
Lowering income inequality and driving green growth by expanding the promise of electric transportation
-
Electric vehicles (EVs) will transform the economics of energy worldwide
-
The ability of EVs to give electricity back to the grid, i.e., bidirectionality, creates economic opportunities for those traditionally left behind
-
Bidirectional EVs will revolutionize people's access to energy while enabling transportation-facilitated economic growth
-
Solutions will look different in developing and developed nations, but the principles remain the same
What We Do
By sharing our research and working directly with public and private organizations we strive to accelerate our journey to a world that is more environmentally and economically sustainable and inclusive.







